

Windows has a few errors scans you can run to find problems in your system. Whatever the source of the problem, you can improve your boot times by troubleshooting, identifying the cause, and fixing it. Reducing the number of tasks Windows has to accomplish on startup can help speed things up.Faulty Drivers: A bad or corrupt driver can increase boot time by creating a hang point while it attempts to start successfully.Corrupted Windows Files: Damaged or missing files in your operating system can also create slower boot times. You can swap a few things around to increase the speed at which your computer starts up.System Overload: You’re trying to load too many programs when Windows starts. While your other hardware plays a role, the hard drive setup is one of the most significant factors in boot times.Wrong Settings: One of your settings isn’t optimized for a fast boot time. Putting your OS on an m.2 drive will make your boot times even faster. Use of an HDD: An operating system installed on an HDD will boot more slowly than on a standard SSD. Then optimize your settings and consider your hardware. The utility will notify you if the scan finds any errors or not.What Causes Slow Boot Times? # How to Fix Slow Boot Times in Windows? #Ĭheck your computer for errors that might increase your boot time. To repair errors without scanning for bad sectors, select the 'Automatically fix file system errors' box and to repair errors and scan for bad sectors, select the 'Scan for and attempt recovery of bad sectors' box.

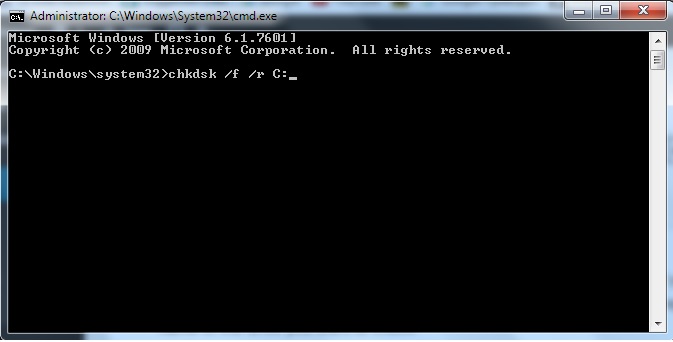
From there click 'Tools' and select 'Check' under the 'Error checking' section. To run Chkdsk from within Windows, but without Command Prompt, you need to go to on 'This PC', right-click on the hard disk you'd like to run the utility on and then click 'properties'. As with the previous command, the volume is the letter of the drive you'd like to repair. To repair errors and scan for bad sectors, type 'chkdsk 'volume': /r' and press enter. To repair errors without scanning for any bad sectors, type 'chkdsk volume :/r' and press enter, where 'volume' is the letter of the drive you'd like to scan, whether it's C or D, or otherwise. Step four: Things begin to get a little more technical here, but you'll need to type 'chkdsk' followed by a specific command to repair any errors you may encounter. Step three: When the Command Prompt window appears, you only need to type 'chkdsk' to begin the scanning process. Step two: Enter 'cmd' into the box and search. Step one: Go to the Start Menu once you've successfully booted your machine and search for the 'run' application. You can either use Recovery Mode, or the original installation medium to boot and then run Command Prompt in order to run Chkdsk this way. Chkdsk can also be run using Command Prompt, if running it from the operating system is not feasible.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
